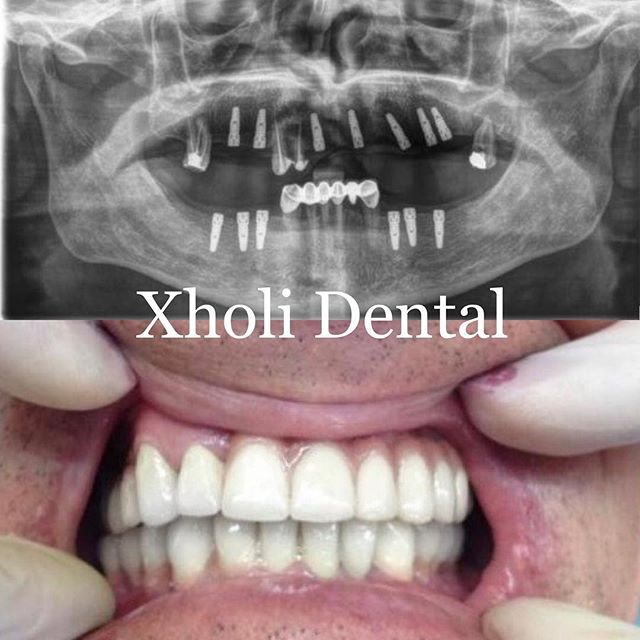
Implantology and Surgery
Dental implants are the artificial root of a tooth that is placed in the bones of the mouth, to add a
missing tooth, or a bridge missing a few teeth. The implants are made of titanium and are fully
biocompatible (appropriate) with the human body. This is an ideal opportunity for people who are left
without one or more teeth. Implants are natural tooth protectors, using implants to avoid the use of
natural teeth for a fixed prosthesis. The success of implants has been proven more than over 28 years
worldwide, where the problem of a lost lump has been resolved forever.
Who are the Benefits of an Implant?
– Keeps the adjacent teeth healthy, to avoid jamming a natural toothpick, leaving them untouched and
healthy.
– Maintenance and non-absorption of the alveolar bone, stimulates the maintenance of the bone as a
root of a natural jaw.
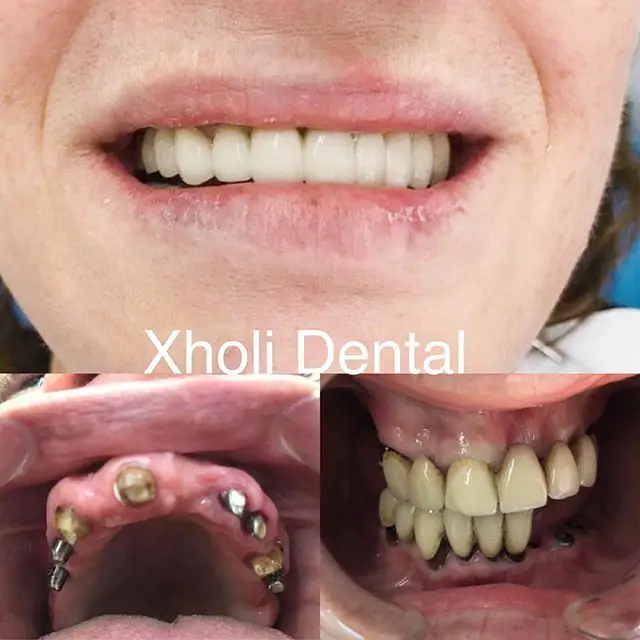
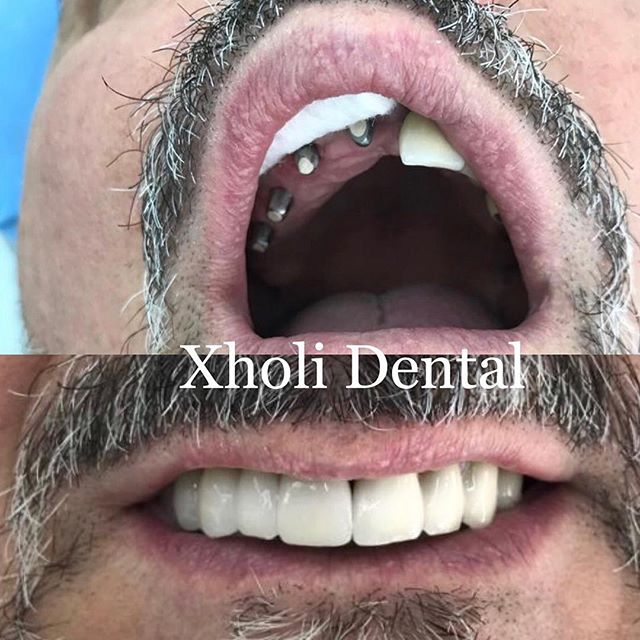
Comparing with a mobile, partial or full prosthetic denture, the advantages are:
– the ability to chew, which is equivalent to that of the natural tooth resulting in nutritional
benefits and digestion, important for all age groups.
– Maintenance of normal facial muscles, with the recovery of a more youthful and natural acne.
– Lack of gingival inflammation and pain associated with the mobility of prosthetics is not present.
– Greater confidence in speech and laughter, with a subsequent increase in quality of life.
What are the patients who can implant the implants?
-Anyone who does not have natural tooth elements and enjoys good health, can generally resort to
implant placement.
-Who has completed the growth phase, typically, 16 years for women, 18 for men.
– Patients who have undergone trauma and have lost some teeth.
– Patients using mobile or total mobile partial dentures.
In which patients is the biggest risk of losing an implant?
-To patients who have a significant bone atrophy (consumption), and where the patient is affected by
systemic illness.
– In patients with paradonthosis (gum disease) and where oral hygiene is very low.
– In diabetic patients (when not regularly treated) as a result of high blood sugar levels, wound infection
may occur, wound closure occurs very slowly, and the implant integration process with the bone may
have problems.
-In patients who smoke or consume too much alcohol, there is a possibility of failure, but in cases where
the implant is successful, they affect its lifespan.
-Any allergic patient to the materials used in surgical intervention.
-The names of menopause, as well as cases of osteoporosis, are more likely to have a positive result on
implants.
How do I proceed with the placement of an implant?
For placement of an implant, initially clinical consultations are seen where many visual details are seen,
then some analyzes such as paronamex, dentalscan, etc., then the patient’s history is made and then
decide on the way the implant treatment is or not.
We have two phases.
The first stage is the surgical phase where the implant is placed in the bone of the mouth.
The second stage is the prosthetic part of the implant.
The advice that a patient needs to know after putting an implant.
Relax: Avoid any physical activity.
Medical Therapy: Follow the course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Pain: After surgery there may be a pain in the operated area; if we have pain we can rely on the use of
proper analgesics.
Bleeding: It may be normal during the first day, a little bleeding when we spit; should avoid foods and
hot drinks in the next 12 hours after the intervention.
Ice: apply ice to the pages at intervals of about 3-4 hours.
Temperature: may experience a slight increase in temperature in the first 48 hours, which may be
normal.
Edema: it is possible that in affected areas it may swell that results in 48 hours; sometimes it may have
the appearance of a hematome that will disappear in about a week.
Oral hygiene: Do not use a toothbrush in the area operated for about two days, simply brush the
neighboring teeth, it is advisable to use detergent fluid such as (listeria, clorexil etc)
Alcohol and tobacco: to avoid for at least 2 weeks, may delay the healing of the wound and be
responsible for post-operative pain.